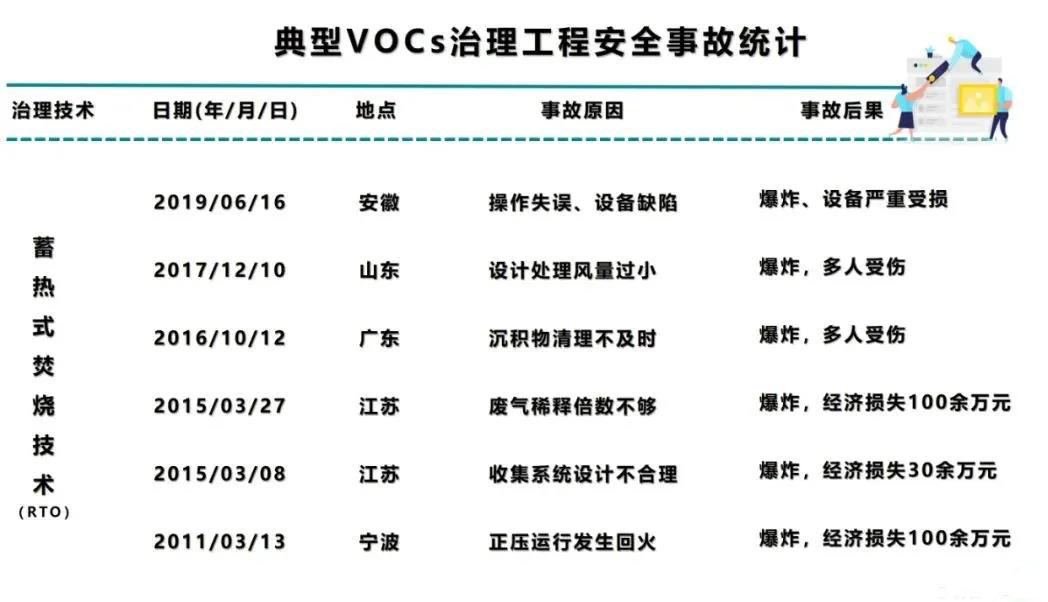
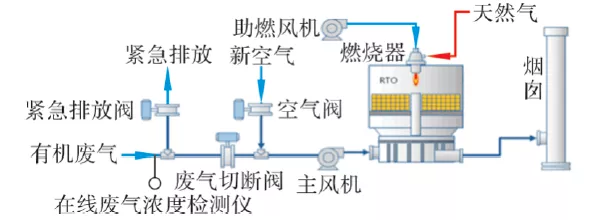
1. In terms of source reduction:
1. Removal: Understand the user's process, clarify the emission characteristics of organic waste gas in the process and the possible unexpected factors to remove the organic waste gas components that are not suitable for entering the RTO. For example, use condensation to recover some high-concentration organic waste gas components; set up water spray The shower device absorbs and scrubs acid and alkali gases to ensure that the organic gas entering the RTO meets the requirements of the intake index, and starts risk prevention from the source.
2. Reduction: Strengthen workshop pretreatment, such as changing normal temperature circulating water to frozen brine to improve condensation efficiency; increase the replacement frequency of absorption circulating liquid, and set up automatic dosing and sewage control to improve absorption efficiency, etc. The total amount of VOCs in the RTO system, thereby reducing the risk of the exhaust gas reaching an explosion.
3. Concentration reduction: A concentration monitor is installed at the inlet of the exhaust gas and the inlet of the necessary exhaust gas branch. When the concentration of the breathing gas of the storage tank and the non-condensable gas of the condenser is high, a dilution air valve is added to the RTO inlet. The concentration of the components under the saturated vapor pressure, and diluted to 25% of the design air volume of the lower explosion limit (LEL); the exhaust gas inlet is equipped with a buffer tank and supplemented with fresh air to ensure that the concentration of the exhaust gas entering the RTO system is lower than its 25% LEL.
Second, the process of prevention:
4. Conducting static electricity: Air ducts, fans and other waste gas conveying equipment and facilities should choose FRP, carbon steel or stainless steel materials with graphite coating as far as possible without corrosion, and bridge and ground them; at the same time, avoid right-angle elbows and elbows Sharp corners prevent the exhaust gas from being exported due to static electricity caused by friction during the conveying process of exhaust gas.
5. Draining liquid: The exhaust gas often forms liquid in the air duct due to the poor demisting effect of the washing tower or the cooling effect. The liquid contains VOCs and continuously volatilizes into the exhaust gas. The concentration increases and must be discharged regularly.
6. Concentration measurement: An online (real-time) concentration detector is set up at a certain distance in front of the RTO system, and it is interlocked with the exhaust gas inlet valve and emergency evacuation valve of the RTO system. The distance is determined according to the response time of the detector. When the exhaust gas concentration exceeds 25% LEL When the exhaust gas inlet valve is closed, the emergency exhaust valve is opened to prevent the high-concentration exhaust gas from entering the RTO system.
7. Ventilation: through forced ventilation measures, meet the minimum ventilation requirements to avoid the accumulation of combustibles, tempering, etc.
8. Explosion venting: Explosion venting valves are installed at certain intervals in the air duct, and the pressure of the venting valve is lower than the stress of the air duct; the pre-washing tower of the RTO system is made of low-strength materials under the condition of ensuring effective use, so that the explosion can occur in time. Relieve pressure and reduce explosion losses.
9. Closed valve: The RTO furnace should be equipped with emergency closing of the intake valve and exhaust valve after the power is cut off to prevent the temperature of the lower part of the regenerator from rising due to the chimney effect.
3. Terminal control
10. Double bypass design: cold bypass and hot bypass are set for the RTO system. The cold bypass is interlocked with the concentration detector, waste gas inlet valve and emergency evacuation valve. When the concentration exceeds 25% LEL, the waste gas inlet valve is closed. , the exhaust gas cannot enter the RTO system; the emergency evacuation valve is opened, and the exhaust gas is discharged after the cold bypass treatment reaches the standard. The hot bypass is interlocked with the fresh air valve, thermometer and pressure gauge. When the temperature and pressure in the RTO furnace are abnormal, the fresh air valve opens, the dilution concentration cools down and reduces the pressure, the hot bypass valve opens, and part of the high-temperature waste gas is directly discharged from the oxidation chamber. The mixer is cooled down and discharged to the chimney to ensure the safe and continuous operation of the RTO system.
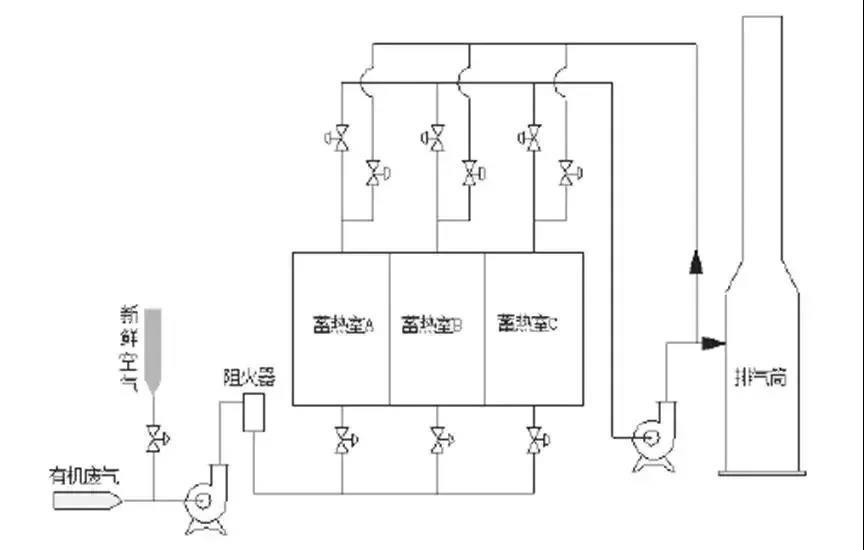
11. Dual-flow field simulation: When designing the RTO furnace, the airflow field and heat flow field are simulated for the exhaust gas. The airflow field simulation ensures that there is no dead angle in the RTO furnace, and the exhaust gas can pass through evenly and smoothly to avoid local turbulence or high concentration; heat flow field The ceramic filling amount is determined by simulation, and the appropriate heat recovery efficiency is selected to avoid the high temperature of the cold end of the regenerator of the RTO furnace and reduce potential safety hazards.
12. Optimize the collection system: standardize the selection of suction hoods and fans. At the same time, the exhaust gas collection pipeline needs to be planned as a whole to form a collection and treatment system of branch pipe → main pipe → treatment device → main exhaust port to ensure the exhaust gas collection effect. For flammable and explosive waste gas, when designing the collection system and pretreatment system, it is beneficial to the safety of the system not to pursue too high strength, but even if the equipment and materials with low strength are selected.
13. Fire resistance: flame arresters, water seals, etc. are installed in the air ducts at the front end of the RTO furnace and the rear end of the production workshop to prevent the explosion and tempering of the RTO furnace or air ducts to the front end or workshop and reduce accident losses.
Flame arrester installation diagram
14. Monitoring: Chain control the RTO system with production, air duct pressure gauges, intermediate fans, concentration detectors, etc., install an online monitoring system and incorporate it into production management monitoring to avoid the disconnect between production and environmental protection, and arrange for special personnel to maintain and manage, such as RTO The concentration of organic matter in the furnace often rises rapidly in a short period of time before the explosion. At this time, if the system is on duty, it can issue an early warning and take necessary measures to avoid accidents. At the same time, an online monitoring system for VOC concentration is installed on the exhaust gas of each RTO system. , to provide necessary data support for enterprise management.